
The Unreal Chimera project will foster a community to establish Unreal Engine as the next-generation tool for GPU-based scientific visualization for modern data on modern hardware.
Education: integration into grade-school, college, and high-school courses on disease and tissue function.Clinical research: precision medicine based on pathology acquired from complete 3D biopsy images, with a focus on cancer research.Biomedical research: comparison of complete organ phenotypes for disease models.Chimera will expand the Unreal Engine into the following areas: Unreal Engine has the potential to become the standard platform for scientific visualization. Low-level access at critical points in the rendering pipeline, enabling integration of domain-specific tools developed by experts for data processing and manipulation.A consistently-updated rendering pipeline, motivated by game developers, to support state-of-the-art tools for interactive graphics, including VR and broad hardware support.Unreal Engine provides an ideal foundation for this platform for two reasons: Our aim is to develop Chimera, an open-source toolkit that supports next-generation scientific data by integrating Unreal Engine's state-of-the-art rendering and virtual reality visualization with modern algorithms for scientific visualization. With the advent of data acquisition methods, such as high-throughput microscopy, the scientific community needs a customizable visualization platform that enables both (1) high-level access to state-of-the-art rendering techniques and (2) direct access to low-level features for developing application-specific tools. This commitment to legacy implementations creates an opportunity, as new scientific visualization based on Unreal would have significant advantages for end users with respect to performance and interface. Further, many of these tools invested in OpenGL version 1.0 twenty years ago and have been reluctant to embrace modern graphics, resulting in a significant gap between commercially-available and academic visualization tools. However, current visualization platforms, such as Imaris, Amira, ParaView, ImageJ, and MeVisLab, lack low-level access to rendering and processing pipelines and provide limited virtual reality (VR) support.


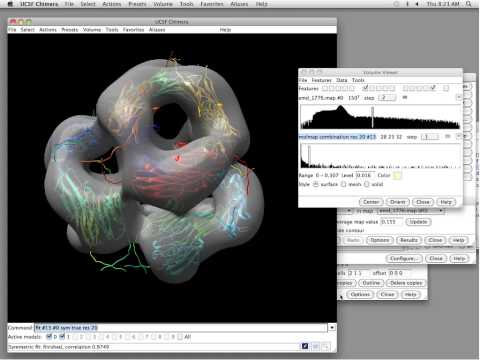
Innovative tools and data structures are therefore required for data manipulation and pre-processing.
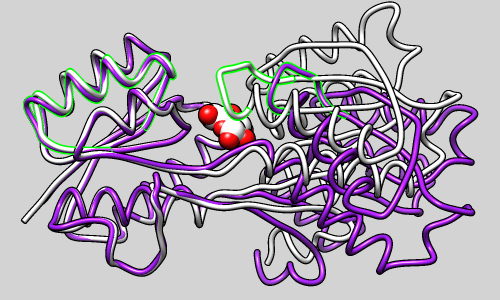
These data sets contain complex structures that are challenging to represent using only explicit geometry or implicit volumes. Next-generation imaging systems and simulations produce multidimensional data at unprecedented rates. Scientific Visualization Needs the Unreal Engine Moreover, the ultimate goal is to enable insight into complex scientific data. Scientific visualization has a strong dependence on computer graphics by integrating modern hardware to facilitate visual analysis, but is ultimately about transforming data to a form that can be rendered. Scientific visualization exploits the spatial properties of data collected from domains such as engineering, climate science, and biomedicine. Visualization is the branch of computer science devoted to analyzing data through visual representation. David Mayerich, 1 Guoning Chen, 1 Hank Childs 2ġUniversity of Houston and 2University of Oregon Project Overview


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
